看網路上大大們的文章和影片,做些紀錄。
以下內容來自網路上大大們的文章。
紀錄程式來源。 稍微修改,print 觀察
程式來源:
二元搜索法(Binary Search)
java测试方法运行时间 System.currentTimeMillis();
[JAVA]記憶體量測與執行時間量測
百萬位元組
整理:
1 currentTimeMillis()返回毫秒時間,返回的值是與1970年1月1日午夜之間的時間差
2 runtime用法還不知道
3 結果不太清楚,用的是雲端環境,看起來是非遞迴比較快,記憶體一樣
遞迴:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
class DivideAndConquer {
static public int Search(int[] array, int num)
{
return Search(array, num, 0, array.length - 1);
}
static public int Search(int[] array, int num, int left, int right)
{
if (left > right)
return -1;
int middle = (right + left) / 2;
if (array[middle] == num)
return middle;
if (array[middle] > num)
return Search(array, num, left, middle - 1);
return Search(array, num, middle + 1, right);
}
}
class Main {
private static final long MEGABYTE = 1024L * 1024L;
public static long bytesToMegabytes(long bytes) {
return bytes / MEGABYTE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int array[] = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,31,33,35,37,39};
int num = 1;
int result = DivideAndConquer.Search(array,num);
for(int i =0;i<=2047483647;i++){
result = DivideAndConquer.Search(array,num);
}
System.out.println(result);
//計算記憶體
// Get the Java runtime
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Run the garbage collector
runtime.gc();
// Calculate the used memory
long memory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
System.out.println("Used memory is byte: " + memory);
System.out.println("Used memory is Megabyte: " + bytesToMegabytes(memory));
//總共花費時間
long stopTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long elapsedTime = stopTime - startTime;
//System.out.println("stopTime: " + stopTime);
System.out.println("總共花費時間:(毫秒)" + elapsedTime);
}
}
0
Used memory is byte: 512384
Used memory is Megabyte: 0
總共花費時間:(毫秒)65118
實機:(改成KB)
Used memory is byte: 707336
Used memory is Kilobyte: 690
總共花費時間:(毫秒) 8413
非遞迴:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Iterative {
static public int Search(int[] array, int num)
{
int left = 0, right = array.length - 1;
while (left <= right)
{
int middle = (right + left) / 2;
if (array[middle] == num)
return middle;
if (array[middle] > num)
right = middle - 1;
else
left = middle + 1;
}
return -1;
}
}
class Main {
private static final long MEGABYTE = 1024L * 1024L;
public static long bytesToMegabytes(long bytes) {
return bytes / MEGABYTE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int array[] = {1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27,31,33,35,37,39};
int num = 1;
int result = Iterative.Search(array,num);
for(int i =0;i<=2047483647;i++){
result = Iterative.Search(array,num);
}
System.out.println(result);
//計算記憶體
// Get the Java runtime
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Run the garbage collector
runtime.gc();
// Calculate the used memory
long memory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
System.out.println("Used memory is byte: " + memory);
System.out.println("Used memory is Megabyte: " + bytesToMegabytes(memory));
//總共花費時間
long stopTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long elapsedTime = stopTime - startTime;
//System.out.println("stopTime: " + stopTime);
System.out.println("總共花費時間:(毫秒) " + elapsedTime);
}
}
0
Used memory is byte: 512328
Used memory is Megabyte: 0
總共花費時間:(毫秒) 48766
實機:(改成KB)
Used memory is byte: 707336
Used memory is Kilobyte: 690
總共花費時間:(毫秒) 8213
其他C/C++的:
【c/c++學習筆記】如何測量一段程式碼的執行時間?
C/C++ 語言測量時間函數,評估程式執行效能方法整理
g++ error: ‘malloc’ was not declared in this scope
可能要加
<stdlib.h>
Binary tree traversal: Preorder, Inorder, Postorder
程式:
https://gist.github.com/mycodeschool/10016271
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node * left;
struct Node * right;
};
void Preorder(struct Node * root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
printf("%d ", root - > data);
Preorder(root - > left);
Preorder(root - > right);
}
void Inorder(Node * root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
Inorder(root - > left);
printf("%d ", root - > data);
Inorder(root - > right);
}
void Postorder(Node * root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
Postorder(root - > left);
Postorder(root - > right);
printf("%d ", root - > data);
}
Node * Insert(Node * root, int data) {
if (root == NULL) {
root = new Node();
root - > data = data;
root - > left = root - > right = NULL;
} else if (data <= root - > data)
root - > left = Insert(root - > left, data);
else
root - > right = Insert(root - > right, data);
return root;
}
int main() {
Node * root = NULL;
root = Insert(root, 9);
root = Insert(root, 4);
root = Insert(root, 8);
root = Insert(root, 7);
root = Insert(root, 18);
root = Insert(root, 1);
//Print Nodes in Preorder.
cout << "Preorder: ";
Preorder(root);
cout << "\n";
//Print Nodes in Inorder
cout << "Inorder: ";
Inorder(root);
cout << "\n";
//Print Nodes in Postorder
cout << "Postorder: ";
Postorder(root);
cout << "\n";
}
結果:
Preorder: 9 4 1 8 7 18
Inorder: 1 4 7 8 9 18
Postorder: 1 7 8 4 18 9
參考:
Binary tree: Level Order Traversal
教學來源:Binary Search Tree: Intro(簡介)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct BstNode {
int data;
BstNode * left;
BstNode * right;
};
//create a new Nod
BstNode * GetNewNode(int data) {
BstNode * newNode = new BstNode();
newNode - > data = data;
newNode - > left = newNode - > right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//insert data in BST
BstNode * Insert(BstNode * root, int data) {
if (root == NULL) {
root = GetNewNode(data);
} else if (data <= root - > data) {
root - > left = Insert(root - > left, data);
} else {
root - > right = Insert(root - > right, data);
}
return root;
}
//search
bool Search(BstNode * root, int data) {
if (root == NULL) {
return false;
} else if (root - > data == data) {
return true;
} else if (data <= root - > data) {
return Search(root - > left, data);
} else {
return Search(root - > right, data);
}
}
// FindMin
int FindMin(BstNode * root) {
if (root == NULL) {
cout << "Error: Tree is empty\n";
} else if (root - > left == NULL) {
return root - > data;
}
// search in left subtree
return FindMin(root - > left);
}
//FindHeight
int FindHeight(BstNode * root) {
if (root == NULL)
return -1;
return max(FindHeight(root - > left), FindHeight(root - > right)) + 1;
}
int main() {
BstNode * root = NULL;
root = Insert(root, 15);
root = Insert(root, 10);
root = Insert(root, 20);
root = Insert(root, 25);
root = Insert(root, 8);
root = Insert(root, 12);
root = Insert(root, 30);
//搜尋數字
int number;
cout << "搜尋數字:\n";
cin >> number;
//結果:
if (Search(root, number) == true) cout << "Found\n";
else cout << "Not Found\n";
//FindMin 找最小值
cout << "最小值:" << FindMin(root - > left) << "\n";
//樹的高度:
cout << "樹的高度:" << FindHeight(root) << "\n";
}
結果:
搜尋數字:
12
Found
最小值:8
樹的高度:3
來源【小馬的資結演算法秘笈】(12) 將infix表達式轉postfix(即普通四則運算式轉逆波蘭表達式)
Infix, Prefix and Postfix
Evaluation of Prefix and Postfix expressions using stack
Infix to Postfix using stack
整理
1
operator -- > 運算子 -->加減乘除
operand -- >運算數 -- >123
2
operator優先順序
1 括號
2 右到左的operator(指數)
3 乘除
4 加減
3
Evaluation of Prefix and Postfix expressions using stack
教學 教了 怎麼計算 postfix
像是 postfix_string = "23-54*+"
創建一個stack S
//由左而右掃描
for i = 0 to length(postfix_string)-1
{
if(postfix_string[i] is operand) //如果是數字:123
Push(postfix_string[i])
else if (postfix_string[i] is operator){ //如果是運算子+-*/
Pop(operand2)
Pop(operand1)
result = operand1 postfix_string[i] operand2 // 先pop的放後面
// 像是(2-3) 變成 23- , 先pop的是3 , 所以就會是2-3
//不過如果是 -23 (prefix) , 先pop的是2 ,但是 還是2-3 (先pop的放前面?)(prefix不知道怎運作)
Push(result)
}
}
return top of stack S
4
Infix to Postfix using stack:
Infix to Postfix using stack
程式碼:
mycodeschool/InfixToPostfix.cpp
有些小錯誤,所以有人修改了:
ms1797/InfixToPostfix.cpp
錯的地方應該就是這邊要加break:
switch(op)
{
case '+':
case '-':
weight = 1;
break;
case '*':
case '/':
weight = 2;
break;
case '^':
weight = 3;
break;
}
還有$符號不知道是什麼,先換成^ (XOR符號???)
結果: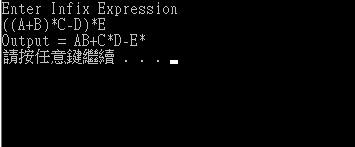
5
Palindrome Number 回文數字
像是abcdcba 或是 121 都是回文
題目:Palindrome Number
題目是判斷數字是不是回文 , 如果是 就true ,不是就false
先踢掉一些狀況
像是 -2(負數) 、 100 (結尾有0 但不是0的數字)
有兩種 回文狀況
12321 或是 1221
範例解答是這樣寫:
int revertedNumber = 0;
while(x > revertedNumber) {
revertedNumber = revertedNumber * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
順序-->
x= 12321 , revertedNumber=0
x= 1232 , revertedNumber=1
x= 123 , revertedNumber=12
x= 12 , revertedNumber=123
順序-->
x= 1221 , revertedNumber=0
x= 122 , revertedNumber=1
x= 12 , revertedNumber=12
最後在判斷
return x == revertedNumber || x == revertedNumber/10;
12==12
或是
12 == 123/10
6
Valid Parentheses
這題是判斷括號正不正確:
([)] 、((()) 這種都是錯的
解法就是用hashmap的方式 , 如果ClosingBracket 對的到 stack top 的 OpeningBracket ,就是true
